Definition of a Router
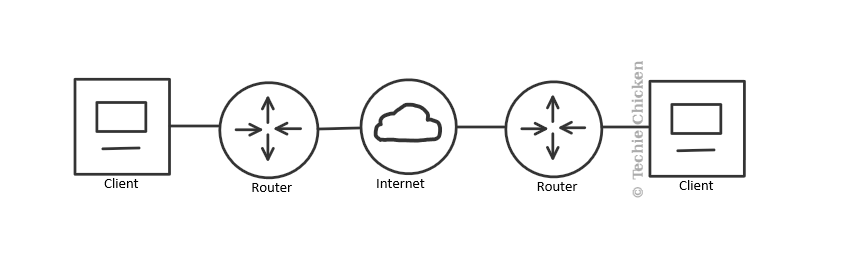
A router is a network device that receives and forwards data packets, allowing two or more computers networks to communicate with each other.
It is a Layer 3 (Network) device on the OSI Model.
Types of Routers
There are several kinds of routers:
Wired Router
It communicates with computers via cable connections.
One port links the router to a modem for data packet reception, while another port connects the router to a computer for data packet transmission.
Wireless Router
It connects in the same way that a wired router does for the reception of the data packets. The only difference is that it sends these data packets through the network using antennas.
Edge Router
It forwards data packets from one network to another but not within a network.
We install it at the “Edge” of a network, where networking devices connect with the Internet.
Core Router
It performs the opposite function of an Edge Router in that it forwards data packets within a network but does not forward them to another network.
It works on the Internet backbone.
vRouter
A virtual router mimics the functionality of a hardware router. You can turn your PC, laptop, or tablet into a virtual router.
Or even better! You can use a VM (Virtual Machine) as a virtual router.
References:
Geek University: What is a router?
It Still Works: What Are the Different Types of Routers?
TechTarget: What’s the difference between an edge router vs. core router?